Rheumatoid Arthritis
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
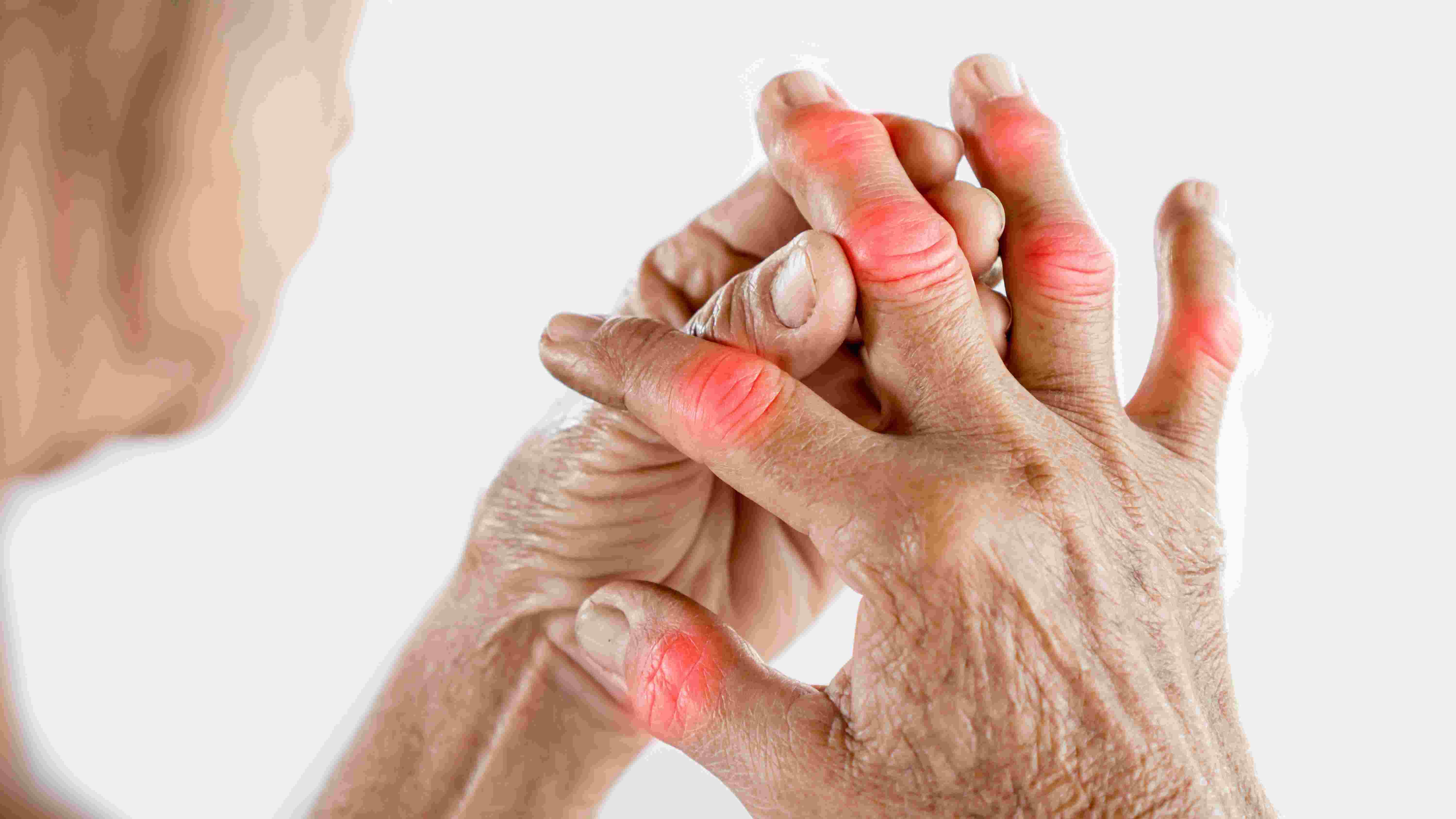
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It causes inflammation, pain, and potential joint deformity. RA can also affect other systems such as the skin, eyes, and lungs.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis:
Common symptoms include joint pain, stiffness (especially in the morning), swelling, and fatigue. RA often affects small joints in the hands and feet first but can progress to larger joints and other organs.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact cause is unknown, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include family history, smoking, obesity, and age (most commonly appearing between 30-60 years old).
Diagnosis and Management:
RA is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, blood tests (such as rheumatoid factor), and imaging studies. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent joint damage and improve quality of life.
Treatment options include medications like disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic agents, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgery may be recommended to manage symptoms and improve joint function.
In conclusion, timely diagnosis and proper treatment are key to controlling Rheumatoid Arthritis. With effective management, individuals can maintain mobility and reduce complications associated with this chronic condition.