Peptic Ulcer Disease, GERD
Understanding Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD) and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) are common gastrointestinal conditions that affect digestion and overall stomach health. Recognizing their symptoms and treatments is crucial for effective management.
Peptic Ulcer Disease:
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inner lining of the stomach and the upper portion of the small intestine. Common symptoms include burning stomach pain, bloating, heartburn, and nausea. Causes may include Helicobacter pylori infection, prolonged NSAID use, and excessive stomach acid production. Treatment often involves antibiotics, acid-reducing medications, and lifestyle changes.
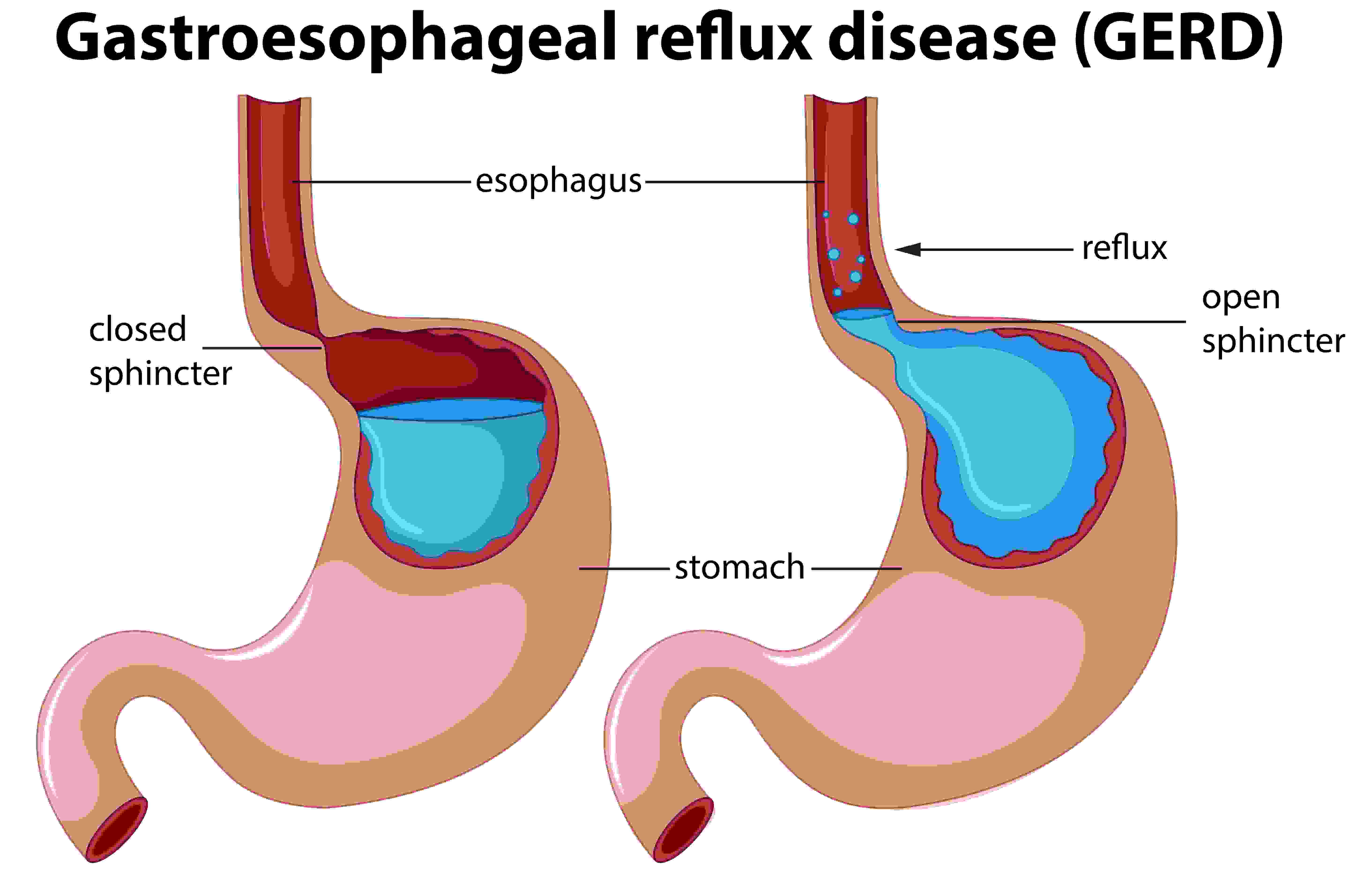
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease):
GERD is a chronic condition in which stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation. Symptoms include heartburn, chest pain, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. GERD may be managed through dietary adjustments, medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), and in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Prevention and Management:
Preventing PUD and GERD involves avoiding spicy and acidic foods, limiting alcohol and tobacco use, and maintaining a healthy weight. Timely treatment of Helicobacter pylori infections and responsible NSAID use are also crucial in preventing peptic ulcers. For GERD, elevating the head during sleep, eating smaller meals, and avoiding lying down right after eating can help reduce symptoms.
In conclusion, understanding Peptic Ulcer Disease and GERD is essential for effective management. Early diagnosis and proper treatment significantly improve patient outcomes and help prevent complications like gastrointestinal bleeding or esophageal damage.